Backflush is a must in gas analysis! Find out what it is used for and how it works.
In gas chromatography, there are different analytical columns allowing the separation of different species. The choice of the column is based on the specific compounds that need to be separated and measured.
One of the best known columns in Micro GC is the molecular sieve also called Molsieve 5A or MS5A. It was specifically designed for the separation of the lightest gases available (permanent gases).
 Column MS5A Capillary
Column MS5A Capillary
It is a very popular column for many applications in both the industry and research laboratories. For instance, it is used to perform hydrogen measurements, studies in catalysis, as well as natural gas and biogas analyses.
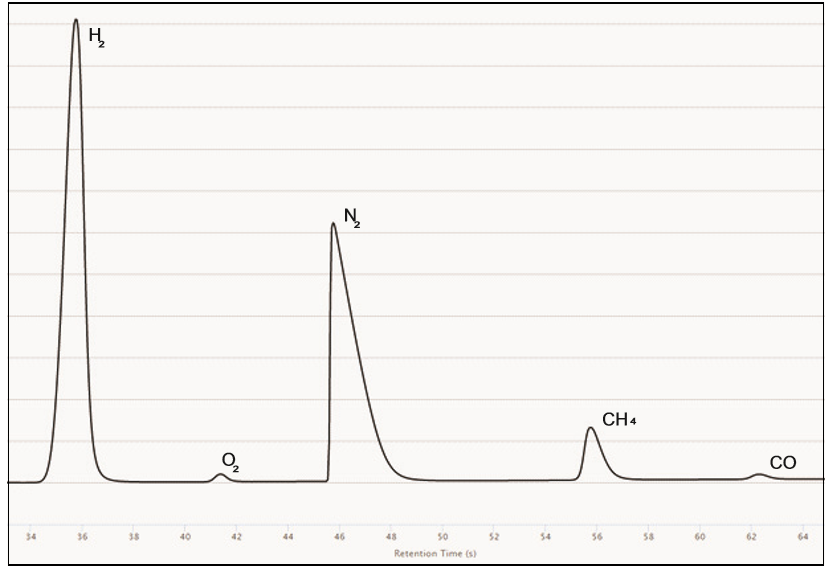
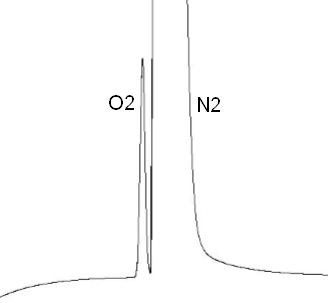
In particular, the molecular sieve allows the analysis of the following gases: helium (He), hydrogen (H2), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), methane (CH4) and carbon monoxide (CO). Depending on the length and efficiency of the column, it is even possible to measure oxygen and argon (difficult separation), without needing sub-ambient temperature.
Nevertheless, the molecular sieve column has a major flaw: it retains a lot of gases that are heavier than permanent gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, ethane, propane, hydrogen sulfur, etc.
Carbon dioxide and water vapor are found in the air around us and in the majority of gas samples that we want to analyze in Micro GC.
Without protection of the MS5A, these heavy compounds will accumulate in the column. In the long run, they will cause lower performances, that can result in the complete loss of chromatographic separation..
Now, let’s get to the the main topic of this article: the Backflush.
What is the purpose of the Backflush?
First and foremost, it is used to protect the column by solely injecting gases compatible with the MS5A, and to stabilize its performances. This will be detailed and illustrated throughout this article.
Second, and this mostly applies to conventional GC, the backflush can reduce the analysis time when the light compounds of interest are in a sample with a complex matrix, composed of heavier compounds.
How does the Backflush work?
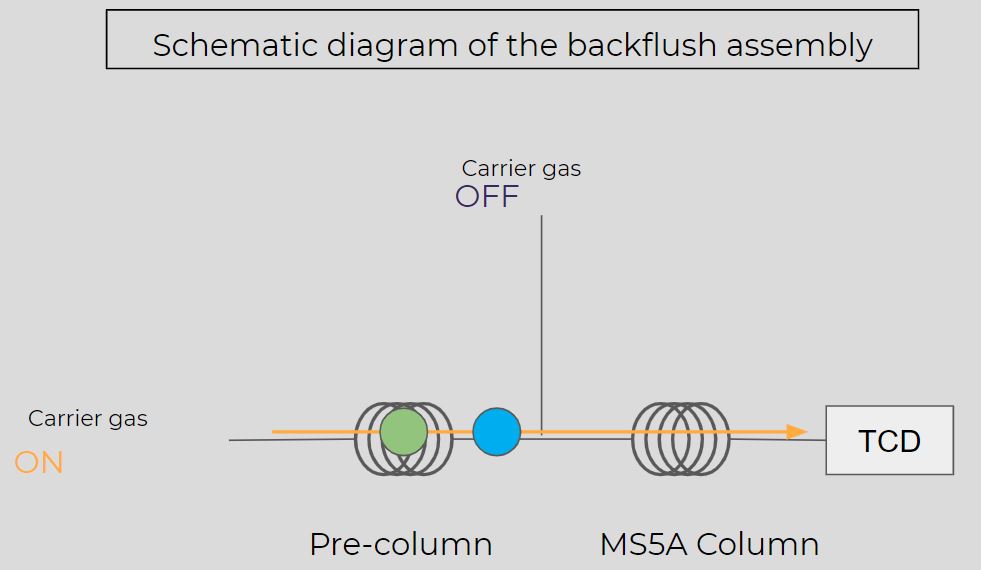
A guard column is used with a stationary phase allowing the retention of water, CO2 and hydrocarbons upstream of the molecular sieve column.
In a first step, this guard column will retain the undesirable compounds and send only the permanent gases into the MS5A. In a second step, with the help of a valve, the guard column will be backflushed to remove the retained gases and prevent any accumulation of heavy compounds in the guard column.
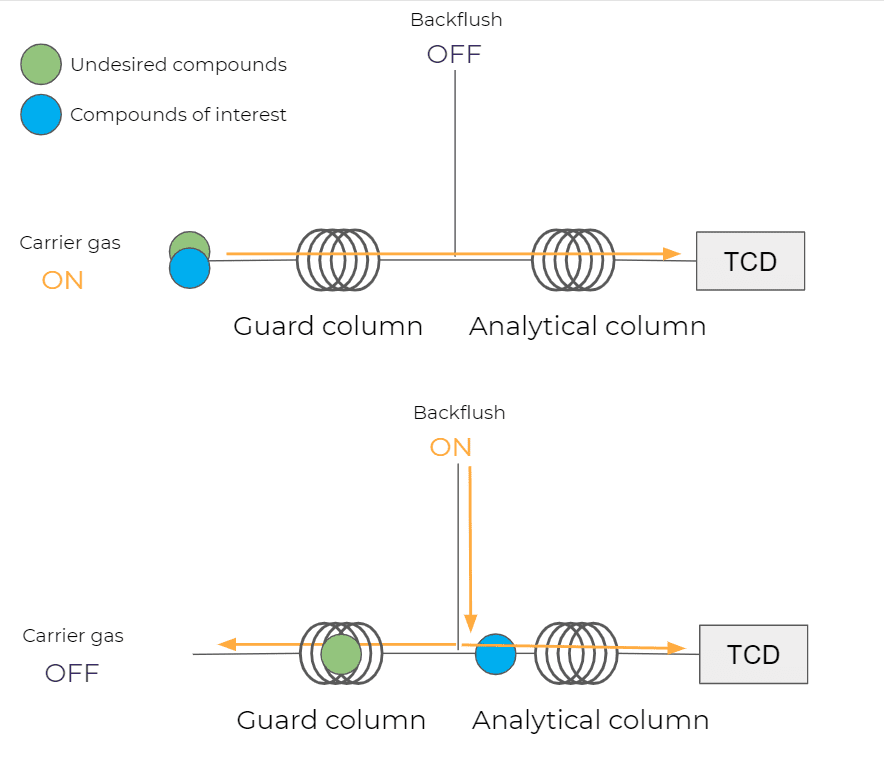
Illustration of the backflush feature
It is with this type of setup that we can protect a column and perform analyses on a gas mixture that contains compounds that are too heavy for the chosen stationary phase.
Now you know how the Backflush works and its role in an analytical system.
In our next article, we will explain how to easily set the Backflush time in order to protect your analytical column.




One Comment