In the field of gas analysis, we are regularly led to follow a process, a reactor or an emission kinetic in time.
Continuous measurement, as close to the gas production as possible, is also called online analysis.

Continuous analysis by automatic sample flow selection
Online analysis
It has many advantages. In particular, it avoids the sampling and handling of the sample which could affect its condition and distort the measurement. Its proximity to the sample allows a follow-up on the composition of a gas over several hours, days or weeks.
Once you start monitoring a sample online, you often want to measure several samples in parallel and continuously. This makes it possible to compare different experiments or to analyze a sample gas at different stages of a process.
Rather than investing in multiple analyzers, one of the most cost-effective solutions is to give a single analyzer the ability to automatically measure multiple gas streams sequentially.
The measurement of multiple gas samples online can be done using a channel selector.

Channel selection valve
Multi-position valve selector
It is a system of one or more automatic valves, close to the analyzer, to minimize the transfer volumes between the valve and the analyzer. There are many types of selection valves, in this article we will mainly talk about flow-through (SF) or dead-ended (SD) rotary selection valves.
SF valves allow a gas flow to be selected while the other unselected channels continue to flow through the valve.
This type of valve has the advantage of easily and quickly bringing a representative sample to the analyzer. However, since the gas flow is constantly circulating, the sample consumption towards the valve is significant. This can be a problem for experiments with small volumes or small gas productions.
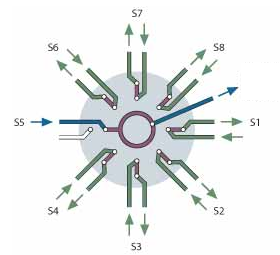
Through-flow valve – SF
SD valves allow a gas flow to be selected without the unselected channels flowing through the valve.
This type of valve allows to limit the consumption of sample gas. However, as the gas flow does not circulate, when passing from one analysis channel to the next, it is necessary to allow time for the selected gas to sweep all the tubing. This is done both upstream and downstream of the valve to ensure that the gas being analyzed is representative. Depending on the volume of the tubes, the flow rate and sometimes the materials used, this can take more or less time.
The risk is to not purge the line properly and to end up with the analysis of a gas suffering from memory effects. The analyzed gas is partly polluted by the previous sample.
The other risk is to obtain a composition of the sample gas different from the composition at time T in the process. In the absence of an efficient sweep (purge), the gas analyzed is the one that was taken well before the selection of the current channel; it is therefore not representative of the current state in the process.
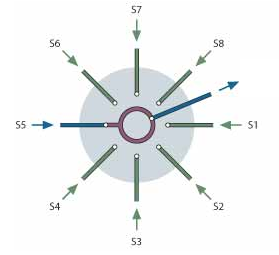
Blocking flow valve – SD
Define your sampling – CHEMLYS to the rescue !
To define a sampling system, it is essential to choose the type of valve and elements. They are selected according to the physicochemical parameters of the sample and its environment. The materials chosen for the transfer of the gas to the analyzer are also very important. If the sample undergoes losses or modifications before arriving at the analyzer, the results obtained will be distorted. For example, one of our articles deals with transfer problems with sulfur products (H2S, Mercaptans, Thiols etc…).
These types of compounds tend to adsorb when passing through stainless steel tubes or during storage. Sometimes it is also important to keep the sample warm during transfer to avoid condensation and protect one’s gas analyzer.
The frequency of measurement per sampling point can quickly become critical if a large number of samples are to be monitored. It is necessary to have a fast and efficient analysis method. In the case of gas chromatography analyzers, we prefer to use FAST GC or MicroGC to perform the analysis of a sample channel in a few minutes.
Please note that the multi-position valves are directly compatible with your Fusion Micro GC. Simply plug them into the USB port on the back of the unit. The valve is then recognized and available in your sequences.
Conclusion :
Automatic sampling is an economical and efficient solution to measure several samples with one analyzer. We must pay great attention to the design of a selection system. It must be adapted to the samples and the environment of the experiment. The materials used, the volumes of the tubes and the type of valve are important parameters to take into account. They guarantee the integrity of the sample and the accuracy of the results.
If you want to learn more about online sampling, CHEMLYS offers a dedicated course.
A bientôt pour des exemples d’échantillonnage automatique. En attendant, n’hésitez pas à nous contacter.




